On January 9, Cell published online the latest research paper entitled Multi-organ Proteomic Landscape of COVID-19 Autopsies by the team of Prof. HU Yu, XIA Jiahong, NIE Xiu of Union Hospital Affiliated to Tongji Medical College and Prof. GUO Tiannan of West Lake University. This paper reports the panorama of protein molecules and pathological changes in multiple organ tissue samples of a patient in critical conditions with COVID-19.

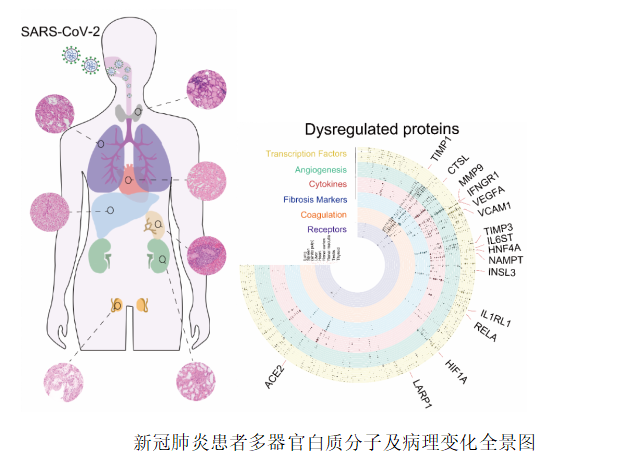
The molecular pathology of multi-organ injuries in COVID-19 patients remains unclear, preventing effective therapeutics development. Here, we report a proteomic analysis of 144 autopsy samples from seven organs in 19 COVID-19 patients. We quantified 11,394 proteins in these samples, in which 5336 were perturbed in the COVID-19 patients compared to controls. Our data showed that cathepsin L1, rather than ACE2, was significantly upregulated in the lung from the COVID-19 patients. Systemic hyperinflammation and dysregulation of glucose and fatty acid metabolism were detected in multiple organs. We also observed dysregulation of key factors involved in hypoxia, angiogenesis, blood coagulation and fibrosis in multiple organs from the COVID-19 patients. Evidence for testicular injuries include reduced Leydig cells, suppressed cholesterol biosynthesis and sperm mobility. In summary, this study depicts a multi-organ proteomic landscape of COVID-19 autopsies that furthers our understanding of the biological basis of COVID-19 pathology.
Paper lingkage: https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(21)00004-0
