On June 23,2023, ZHAO Jun 's research group from Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology published a research paper entitled " Simultaneous Delivery of Dual Inhibitors of DNA Damage Repair Sensitizes Pancreatic Cancer Response to Irreversible Electroporation " ( co-delivery of dual DNA damage repair inhibitors to sensitize pancreatic cancer to irreversible electroporation treatment response ) in the classic journal of nanoscience ' ACS Nano ' ( Chinese Academy of Sciences Area 1 Top, IF 18.027 ). It reveals a new strategy for the comprehensive treatment of pancreatic cancer.

Pancreatic cancer is known as the ' king of cancer ', with hidden early symptoms and lack of effective treatment. The 5-year survival rate of patients is less than 9 % for a long time. Irreversible electroporation ablation ( IRE ), also known as ' nanoknife ', is a minimally invasive interventional therapy that releases high-voltage electrical pulses by inserting a needle electrode into the tumor, permanently destroying the cell membrane and killing cancer cells. IRE has been approved for clinical treatment of pancreatic cancer. However, during IRE ablation, the distribution of pulsed electric field intensity inside the tumor is not uniform ; when the electric field intensity is lower than the killing threshold, the tumor cells are only temporarily disturbed, which can survive after IRE and eventually lead to tumor recurrence. Effective removal of these residual tumor cells is of great significance for reducing the risk of tumor recurrence after IRE and achieving long-term survival of pancreatic cancer patients.
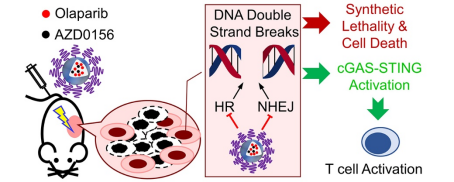
The group found that although the low-intensity pulsed electric field could not kill the tumour cells, it still induced DNA double-strand damage in the tumour cells and activated the DNA Damage Repair (DDR) signalling pathway. Combining the PARP inhibitor Olaparib and the ATM inhibitor AZD0156 could inhibit both homologous recombination (HR) and non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) DNA damage repair pathways in tumour cells, significantly reducing their recurrence potential after electric pulse treatment. The group then designed a tumour-penetrating drug delivery platform (M-TK-OA) with ROS-responsive properties to achieve efficient drug delivery to pancreatic tumours.IRE combined with M-TK-OA showed superior efficacy in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer and activated CD8+ T-cell-mediated anti-tumour immune response. At the same time, the cGAS-STING innate immune signalling pathway was also activated and partially contributed to the efficacy of IRE combined with M-TK-OA. The present study demonstrated that the use of nano-agents to inhibit both PARP- and ATM-mediated DNA damage repair behaviours could effectively sensitize the therapeutic response of pancreatic cancer to IRE, providing a useful new idea for the clinical treatment of pancreatic cancer patients.
The first completion unit of the paper is the Basic Medical College of Huazhong University of Science and Technology. Dr. LONG Xin of Basic Medical College and DAI Anna, a graduate student of 2020, are the co-first authors of the paper. Professor ZHAO Jun, Professor ZHU Xiaohua of the Department of Nuclear Medicine, Tongji Hospital, and Professor LI Chun of the Anderson Cancer Center were the co-authors of the paper. This research is supported by Hubei Outstanding Youth Fund, National Natural Science Foundation of China and Huazhong University of Science and Technology.
Paper link:https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.3c05009
