Recently, the research team led by Professor YANG Wei has made significant strides in the field of exosome regulation of muscle growth and aging, as well as the relationship between muscle loss and the risk of all-cause mortality. Supported by key national research and development plans, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation, and the Biostime Nutrition Fund, the team has published three consecutive research papers in the international professional journals "Journal of Nanobiotechnology" (IF5y = 11.5) and "Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle" (IF5y = 10.7).
Professor YANG Wei served as the corresponding author for the papers, with the first authors being PhD students MENG Zitong (class of 2020), and ZHOU Xiaolei and ZHOU Huanhuan (both class of 2022). The School of Public Health at Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, is recognized as the first author's affiliation.
Paper One: "Gouqi-derived nanovesicles (GqDNVs) inhibited dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy associating with AMPK/SIRT1/PGC1α signaling pathway," published in the Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2024). The research explores the potential of Goji berry-derived nanovesicles to combat muscle atrophy, a condition often associated with the use of corticosteroids like dexamethasone.
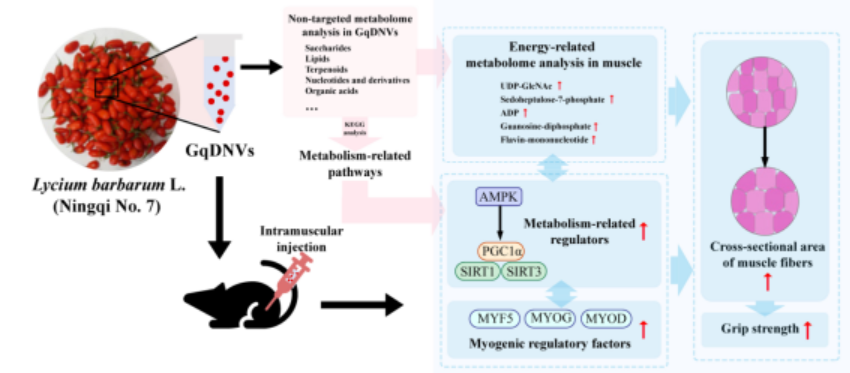
Figure 1: Summary schematic of the extraction process of LBP exosomes, non-targeted/targeted metabolomics to detect the type and content of LBP exosome contents, and changes in the expression level of the AMPK/SIRT1/PGC1a signalling pathway after intramuscular injection of LBP exosomes, as well as changes in the involvement of the regulation of muscle phenotypes.
Paper Two: "Human milk extracellular vesicles enhance muscle growth and physical performance of immature mice associating with Akt/mTOR/p70s6k signaling pathway," published in the Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2023). This study investigates the role of human milk extracellular vesicles in enhancing muscle growth and physical performance in immature mice, providing insights into potential applications for muscle health and development.
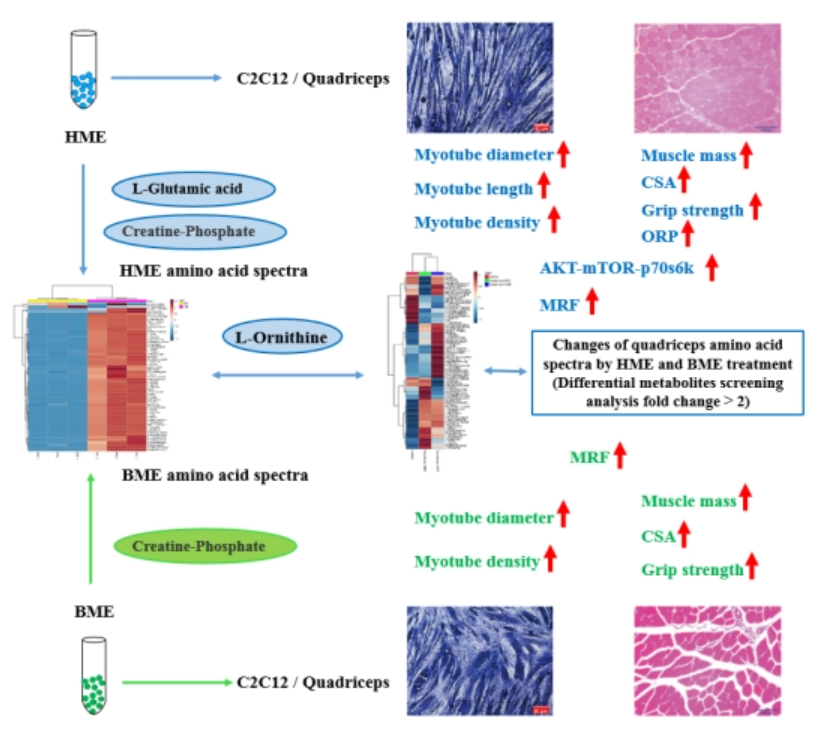
Figure 2: Summary schematic of the mechanisms by which human (HME)/bovine (BME) milk-derived exosomes regulate skeletal muscle development/aging.
Paper Three: "Association of muscle wasting with mortality risk among adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies," published in the Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle (2023). This systematic review and meta-analysis examines the link between muscle wasting and the risk of mortality, highlighting the importance of early detection and intervention in chronic diseases to reduce mortality rates and promote healthy longevity.
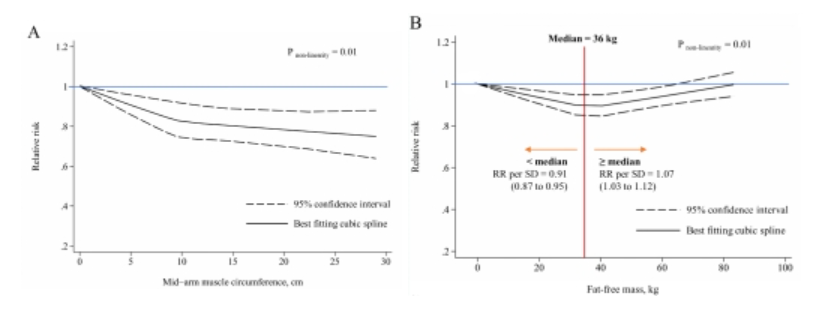
Figure 3: Dose-response plots of upper arm circumference and lean body mass in relation to all-cause mortality
The findings from these papers underscore the innovative approaches to addressing muscle aging and loss, with potential implications for the development of therapeutic strategies to improve muscle health and extend active life spans.
For More Information:
[1] Xiaolei Zhou, Shiyin Xu, Zixuan Zhang, Mingmeng Tang, Zitong Meng, Zhao Peng, Yuxiao Liao, Xuefeng Yang, Andreas K. Nussler, Liegang Liu, Wei Yang*. Gouqi-derived nanovesicles (GqDNVs) inhibited dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy associating with AMPK/SIRT1/PGC1α signaling pathway. Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2024) 22:276.
[2] Zitong Meng, Dong Zhou, Dan Lv, Quan Gan, Yuxiao Liao, Zhao Peng, Xiaolei Zhou, Shiyin Xu, Penglong Chi, Zhipeng Wang, Andreas K. Nüssler, Xuefeng Yang, Liegang Liu, Dongrui Deng, Wei Yang*. Human milk extracellular vesicles enhance muscle growth and physical performance of immature mice associating with Akt/mTOR/p70s6k signaling pathway. Journal of Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Aug 29; 21(1): 304.
[3] Huan-Huan Zhou, Yuxiao Liao, Zhao Peng, Fang Liu, Qi Wang, Wei Yang*. Association of muscle wasting with mortality risk among adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Journal of cachexia, sarcopenia and muscle. 2023 Aug;14(4):1596-1612.
Contact: For further inquiries or to request an interview with Professor Yang Wei or the research team, please contact the School of Public Health at Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology.
